Flood prevention, dike and levee monitoring
Continuous and effective monitoring and surveying of flood prevention dikes and levees are more and more important.
Non-destructive geophysical surveying (water and land seismic measurements, geoelectric tomography and ground radar surveys) of dikes and their surroundings provide a quick and reliable solution to this problem. With these measurements one can obtain an overall picture about the condition of the dike section being investigated. The causes behind cracks for example can be revealed, while investigation of the surroundings can pinpoint those locations where potential sub-dike leakage and water jets could develop.
Critical section of the dike can be determined, which makes it possible to prevent a potential dike failure.
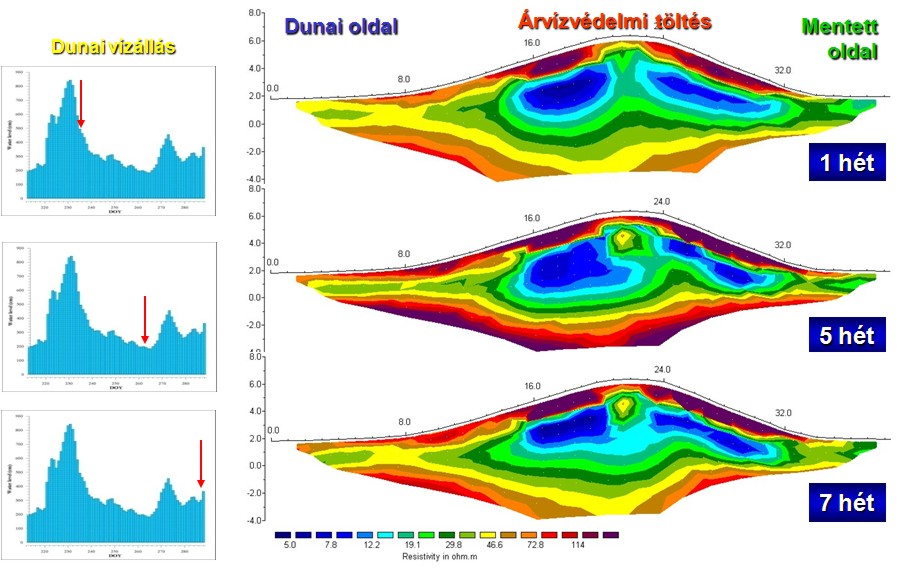
By performing measurements at different water levels the periodical saturation and mechanical changes within the dike and its surrounding can be monitored.
Dike investigations along river Kőrös
Using non-destructive geophysical measurements (in this case ground radar as well as water and land seismic surveyings) Geomega investigated the flood prevention dike along river Körös.
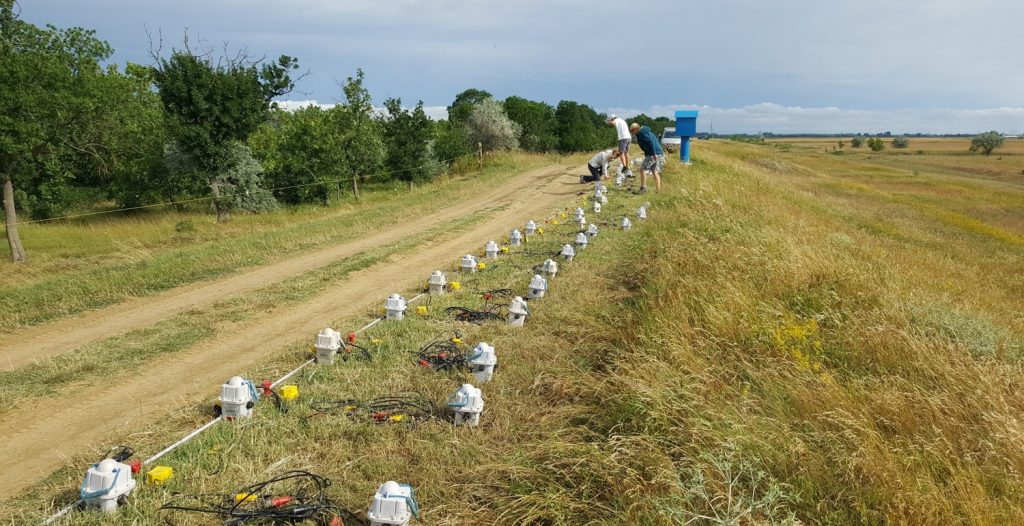
The figure below (photo on the left) shows the receivers of the high resolution seismic spread as well as a blue artificial object (part of the draining system) constructed on the dike (in the background).
On the site seismic reflection and MASW surveying were conducted. The results of these measurements are shown on the right, where the S-wave velocities obtained from Rayleigh type surface waves are overlain on the seismic section. The effect of the blue object can be seen both on the velocity values of the MASW surveys (as a velocity anomaly) and on the seismic section as a disturbed pattern in the middle. On the seismic section the layering of the dike structure can also be seen.

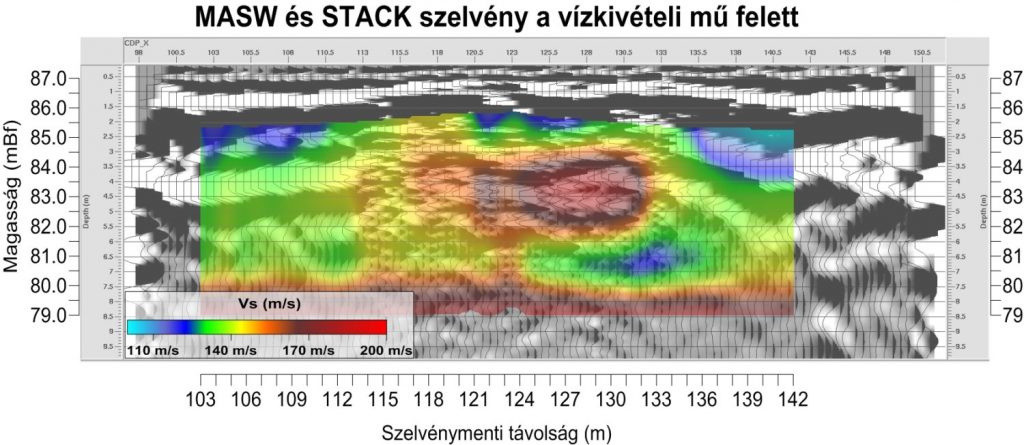
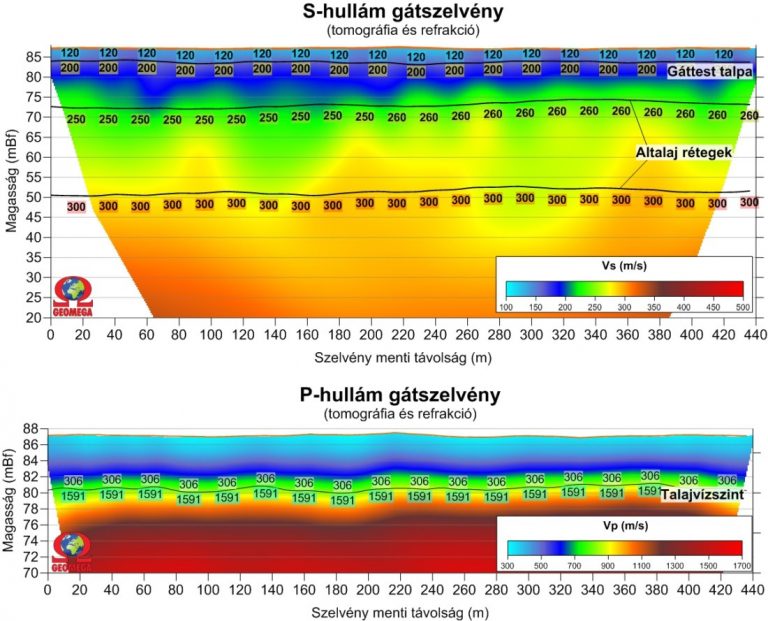
Lower resolution but deeper penetration P and S-wave surveys were also recorded during this project.
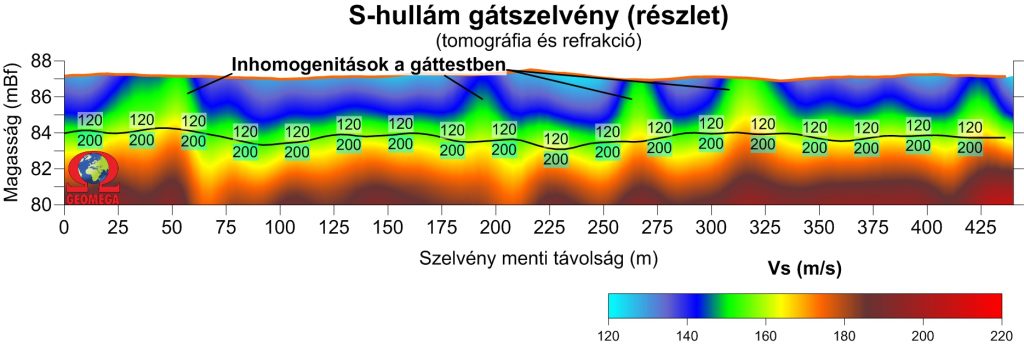
On the image below the tomographic image of the S-wave velocity distribution along the dike is shown, focusing on the upper few meters. The figure demonstrates that above the base of the dike (found approximately at 84m above sea level) there are several seismic velocity anomalies within the dike body.